CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT
Continuous Improvement is an ongoing process of making incremental enhancements to products, services, or processes to boost efficiency, quality, and effectiveness.
Continuous Improvement:
Driving Efficiency in Printing and Flexible Packaging Industries
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, the concept of continuous improvement (CI) has become essential for companies striving to enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and improve product quality. Rooted in methodologies like Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, and Kaizen, continuous improvement is a structured approach that promotes small, incremental changes over time, leading to significant improvements in overall operations. In industries such as printing and flexible packaging, where precision, cost control, and speed are critical, continuous improvement plays a vital role in maintaining profitability and staying ahead of competitors.
Understanding Continuous Improvement in Manufacturing
Continuous improvement is a philosophy that focuses on regularly evaluating processes, identifying inefficiencies, and implementing changes to optimize production. Unlike large-scale transformations that require major capital investments, continuous improvement emphasizes ongoing, incremental modifications that lead to sustainable progress over time.
The CI approach is particularly relevant in manufacturing industries, where even minor adjustments in workflow, material usage, or machine performance can result in significant cost savings and higher product quality. Tools like Total Productive Maintenance (TPM), 5S, and Statistical Process Control (SPC) are commonly used to streamline operations and reduce waste.
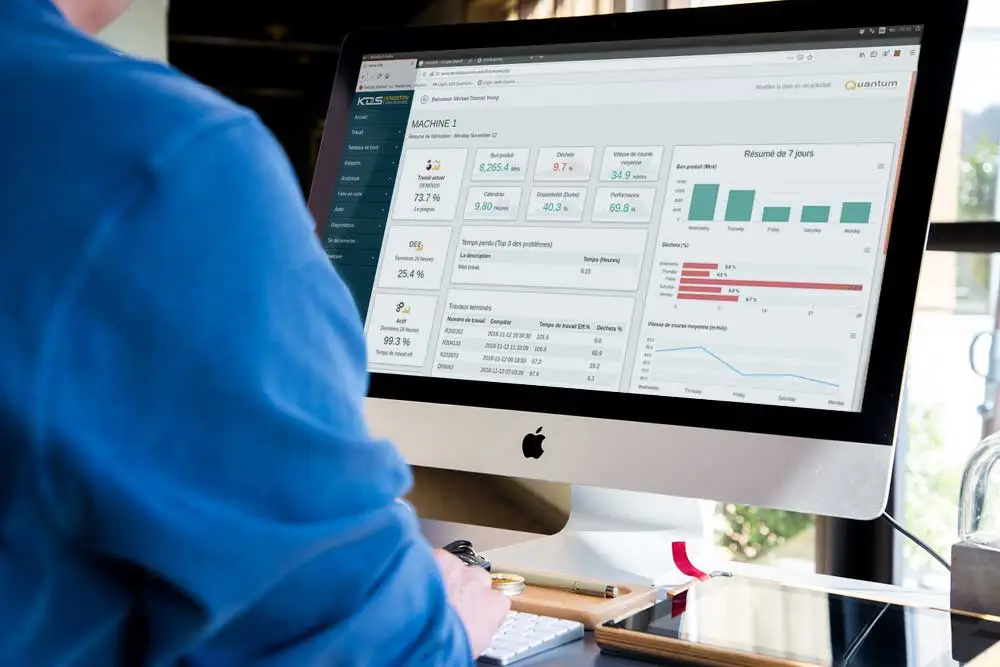

Real-time monitoring systems, such as, KDS’ Quantum Efficiency Management System, automatically track labor and substrate usage on production machinery and can help manufacturers identify excessive consumption patterns and adjust their processes to optimize machine utilization.
The Role of Continuous Improvement in the Printing and Flexible Packaging Industries
The printing and flexible packaging sectors face unique challenges, including fluctuating raw material costs, stringent quality standards, and high customer expectations for customization and quick turnaround times. Implementing CI strategies in these industries ensures smoother workflows, higher efficiency, and reduced operational costs.
1. Reducing Waste and Material Costs
Printing and packaging processes often generate significant material waste due to inefficiencies in design, printing errors, or machine downtimes. CI methodologies such as Lean Manufacturing and the 5S System (Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain) help companies minimize waste by improving inventory management, enhancing machine maintenance, and reducing overproduction.
For example, adopting real-time monitoring systems, such as, KDS’ Quantum Efficiency Management System, to track labor and substrate usage can help manufacturers identify excessive consumption patterns and adjust their processes to optimize material utilization. Additionally, implementing standardized color management and quality control measures reduces the risk of print defects, lowering rework and material waste.
2. Enhancing Machine Efficiency and Reducing Downtime
Equipment performance is a key factor in the printing and flexible packaging industries. Machine breakdowns or inefficiencies can lead to costly production delays and missed deadlines. Total Productive Maintenance (TPM), a continuous improvement methodology, focuses on preventive and predictive maintenance to ensure that equipment operates at peak performance.
By regularly maintaining and monitoring machines, manufacturers can prevent unexpected breakdowns, extend equipment lifespan, and reduce downtime. Implementing automated diagnostic tools and predictive analytics further enhances this process, allowing maintenance teams to detect potential failures before they occur.
3. Improving Workflow and Employee Productivity
CI is not limited to machinery and materials; it also focuses on optimizing human resources. Training employees in Lean principles, Six Sigma techniques, and standardized operating procedures ensures a culture of CI within the organization.
For instance, implementing Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) and cross-training workers on multiple processes enhances flexibility in the workforce, allowing for quicker response times to production changes or unexpected bottlenecks. Encouraging employee feedback and participation in improvement initiatives fosters a culture where workers actively seek ways to refine processes and eliminate inefficiencies.
4. Implementing Digital and Smart Manufacturing Technologies
The rise of Industry 4.0 and digital transformation has introduced new opportunities for continuous improvement in the printing and flexible packaging industries. Smart manufacturing technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud-based systems, provide real-time data and analytics that help manufacturers make informed decisions to optimize production.
For example, IoT-enabled printing presses can monitor production parameters in real time, automatically adjusting settings to minimize defects and improve efficiency. AI-driven quality control systems can detect inconsistencies in printing or packaging, reducing the risk of defective products reaching customers.
Case Study: Successful Continuous Improvement Implementation in Flexible Packaging
A leading flexible packaging manufacturer adopted a Kaizen-based continuous improvement strategy to reduce waste, improve machine efficiency, and enhance product consistency. By implementing regular team workshops and using data analytics to monitor print defects, the company achieved a 20% reduction in material waste and a 15% improvement in machine uptime within a year. Moreover, employee engagement increased, leading to more proactive problem-solving on the production floor.
Conclusion
Continuous improvement is an essential strategy for manufacturers in the printing and flexible packaging industries. By implementing Lean principles, enhancing machine efficiency, optimizing workflows, and leveraging digital technologies, companies can achieve higher productivity, lower costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
As market demands evolve and competition intensifies, businesses that embrace a culture of continuous improvement will be better positioned for long-term success. Whether through small incremental changes or breakthrough innovations, the journey of continuous improvement remains a key driver of growth and sustainability in the manufacturing sector.
Our Happy Customers